japanese beetle life cycle chart
In most climates Japanese beetles have a one-year life cycle. Japanese Beetle Life History Japanese beetle has a one year life cycle.

Japanese Beetle Life Cycle Identify Japanese Beetles Orkin
They then emerge in spring where the beetle life cycle starts over again.

. The head and thorax are. Usually the colorful beetles are most active during warm summer days. The egg larva and pupa life cycle stages develop underground and unless soil is removed or dug into these life stages will not be seen.
Japanese beetles are a type of scarab that are pests. Adult Japanese beetles spend nights on the shrubs and trees where they feed. Adult beetles begin to emerge from the soil as early as the third week of May in the warmer climates and throughout June in.
The males usually are slightly smaller than the females. Lifecycle of the Japanese beetle. But the best time to handpick the destructive beetles from shrubs bushes and trees is in cool mornings when they are less active and easier.
An individual Japanese beetle lifespan is about 30 to 45 days. Observing Japanese beetles feeding on plants is quite common since the adult beetle feeds on about 300 species of trees shrubs ornamental and. Ova are laid individually or in small clusters near the soil surface.
MayJune beetles have a two to three-year life cycle grub stage from August through the next year and. When temperatures exceed 35 C and relative humidity is greater than 60 flight ceases. Late June through August or September.
Adults may begin to emerge from the soil in early June and are usually most abundant in. Leaves of plants such as birch canna crape myrtles grapes hops linden trees rose bushes etc. Life Cycle There is only one generation per year.
The Japanese beetle has four stages in its life cycle two of which can be destructive to your lawn and garden. Most of the beetles life is. The female beetle can begin laying her eggs within 24 hours of emergence.
Life Cycle of the Japanese Beetle. Adult beetles start to emerge from. Japanese Beetle Life History Japanese beetle has a one year life cycle.
Larvae feed on roots underground while adults feed on leaves and stems. The beetle has six small tufts of white hair along the sides and back of its body under the edges of its wings. However some adults may be found into September.
When these conditions are met Japanese beetles emerge from their winter hiding spots in early- to mid-summer. During the feeding period females intermittently leave plants. Japanese beetles are similar to other Junebugs in appearance and 38 inch long and 14 inch wide.
They then dig a new chamber next to where they found the beetle and stash it in the new room before laying eggs. In Iowa adult beetles emerge in mid-June through July.

Beetle Identification A Guide To Common Species With Photos Owlcation

Japanese Beetle And Grub Control Gardener S Edge

Identification Biology Ppt Video Online Download

Japanese Beetle Popillia Japonica Coleoptera Scarabaeidae Clemson University Entomology Dept Mature Adult Larva Ppt Download

June Bug Introduction Life Cycle Remedies
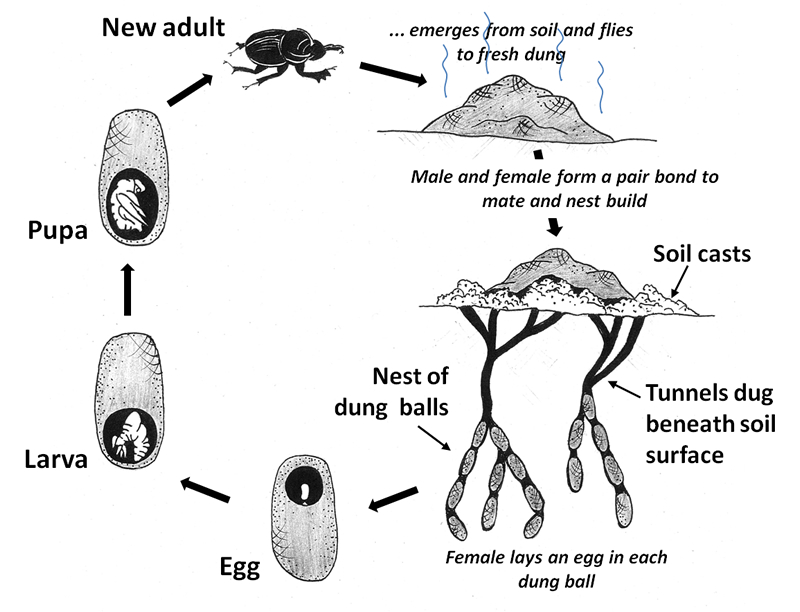
Benefits Of Dung Beetles On Horse Properties Equine Permaculture
Expert Project Management Effective Data Visualization Book Review

How To Get Rid Of Japanese Beetles In The Garden Garden Fundamentals
Japanese Beetle Management In Minnesota

Japanese Beetles The Morton Arboretum

Japanese Beetles And Controlling Them Hoffmann Hillermann Nursery Florist

How To Get Rid Of Japanese Beetles In The Garden Garden Fundamentals

Time To Watch Out For The Japanese Beetle Alabama Cooperative Extension System
Grubs And The Japanese Beetle Sterling Insect Lawn Control Inc
Darkling Beetle Teaching Resources Teachers Pay Teachers

Billbugs And White Grubs Control In Home Lawns 5 516 Extension

The Spring Tiphia A Natural Enemy Of The Japanese Beetle Integrated Pest Management

